Review sheet histology of nervous tissue – Embark on a journey into the intricate realm of nervous tissue histology, where the intricate tapestry of cells, structures, and functions unfolds before our eyes. This review sheet serves as an indispensable guide, providing a comprehensive overview of the histological techniques, structural organization, and pathological manifestations of this fascinating tissue.
1. Introduction
Histology, the study of tissues at the microscopic level, plays a pivotal role in understanding the structure and function of nervous tissue. A review sheet for histology of nervous tissue provides a comprehensive guide to the diverse cell types, structural organization, and staining techniques used in its analysis.
2. Tissue Preparation and Staining Techniques
Preparing nervous tissue samples for histological analysis involves a series of techniques to preserve and enhance their cellular components. Common methods include fixation, dehydration, embedding, and sectioning. Staining techniques, such as hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), Nissl staining, and immunohistochemistry, highlight specific cellular structures and molecules, aiding in their identification and characterization.
3. Structural Organization of Nervous Tissue
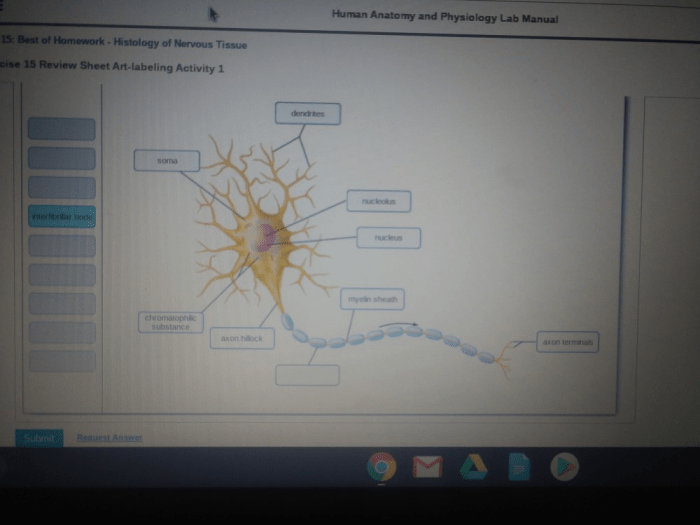
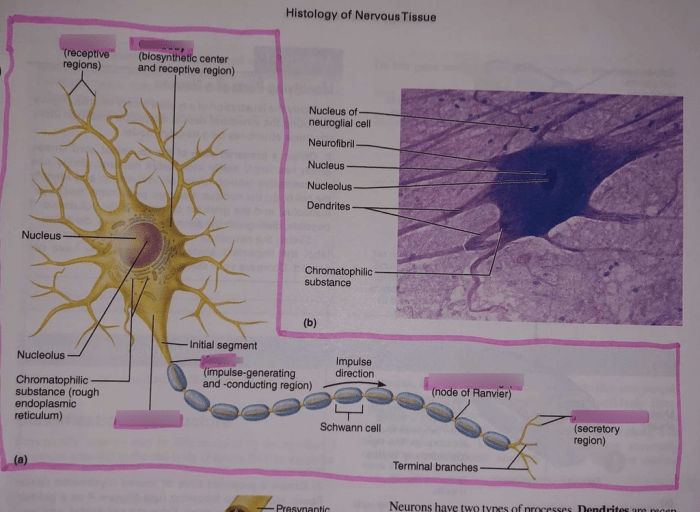
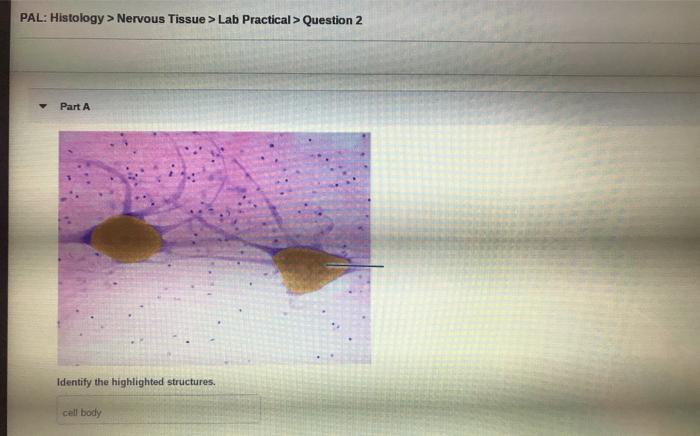
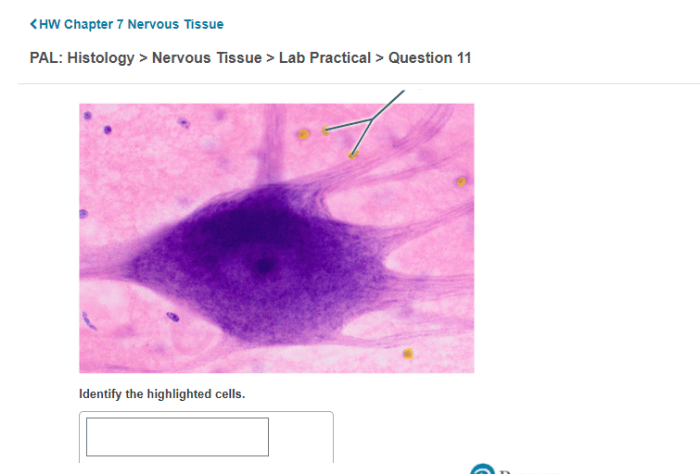
Cell Types, Review sheet histology of nervous tissue
Nervous tissue consists of two main cell types: neurons and glia. Neurons, the functional units of the nervous system, are responsible for transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals. Glia, including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia, provide structural support, insulation, and nourishment to neurons.
Neuron Doctrine and Neural Circuits
The neuron doctrine establishes the neuron as the fundamental unit of the nervous system, with dendrites receiving signals, the cell body integrating them, and the axon transmitting signals to other neurons. Neural circuits, interconnected networks of neurons, form the basis of complex brain functions.
4. Histological Features of Nervous Tissue Regions
Different regions of the nervous system exhibit unique histological characteristics. The brain, for instance, has a complex layered structure with distinct areas responsible for specific functions. The spinal cord, on the other hand, is organized into a central canal surrounded by gray and white matter.
Peripheral nerves are composed of bundles of myelinated and unmyelinated axons.
| Region | Key Histological Features |
|---|---|
| Brain | – Layered structure with distinct areas
|
| Spinal Cord | – Central canal surrounded by gray matter (cell bodies) and white matter (axons)
|
| Peripheral Nerves | – Bundles of myelinated and unmyelinated axons
|
Top FAQs: Review Sheet Histology Of Nervous Tissue
What is the significance of histology in studying nervous tissue?
Histology provides a detailed understanding of the cellular and structural components of nervous tissue, enabling researchers and clinicians to visualize and analyze the intricate organization and function of this complex tissue.
How does a review sheet assist in histology of nervous tissue?
A review sheet serves as a concise and structured guide, summarizing the key histological features and techniques used in the study of nervous tissue. It provides a valuable resource for students, researchers, and medical professionals seeking a comprehensive overview of this field.