Dive into the fascinating world of wave phenomena with the Gizmo Ripple Tank Answer Key. This comprehensive guide unlocks the mysteries of ripple tanks, revealing their purpose, mechanics, and applications in a captivating and accessible manner.
From understanding the principles of wave propagation and interference to exploring real-world applications in various fields, this answer key provides a comprehensive overview of ripple tank technology.
Gizmo Ripple Tank
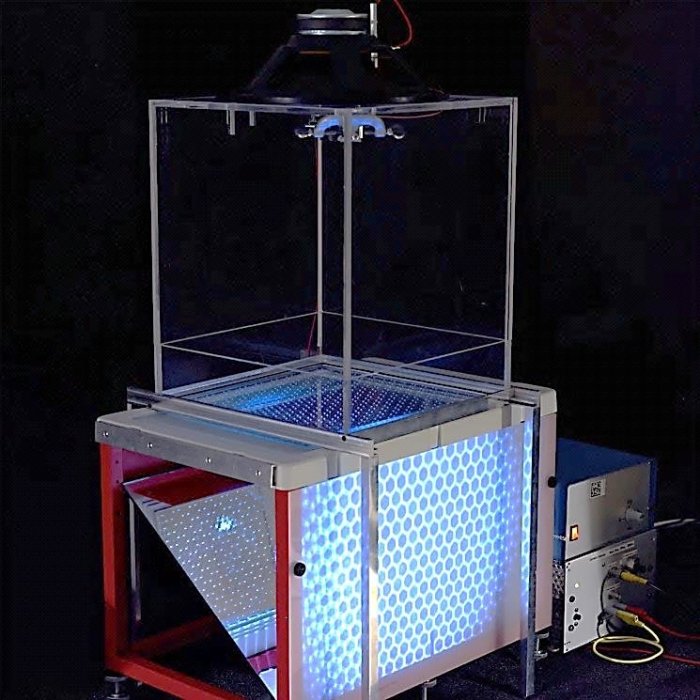

A ripple tank is a device that demonstrates the propagation of waves.
It consists of a shallow tank of water with a wave generator at one end. The wave generator creates waves that travel across the surface of the water. The waves can be reflected, refracted, or diffracted by obstacles placed in the tank.
Gizmo Ripple Tank Simulation
The Gizmo ripple tank simulation is a computer simulation of a ripple tank. It allows you to create and observe waves in a ripple tank. You can change the frequency, amplitude, and wavelength of the waves. You can also add obstacles to the tank to see how they affect the waves.
Gizmo Ripple Tank Answer Key
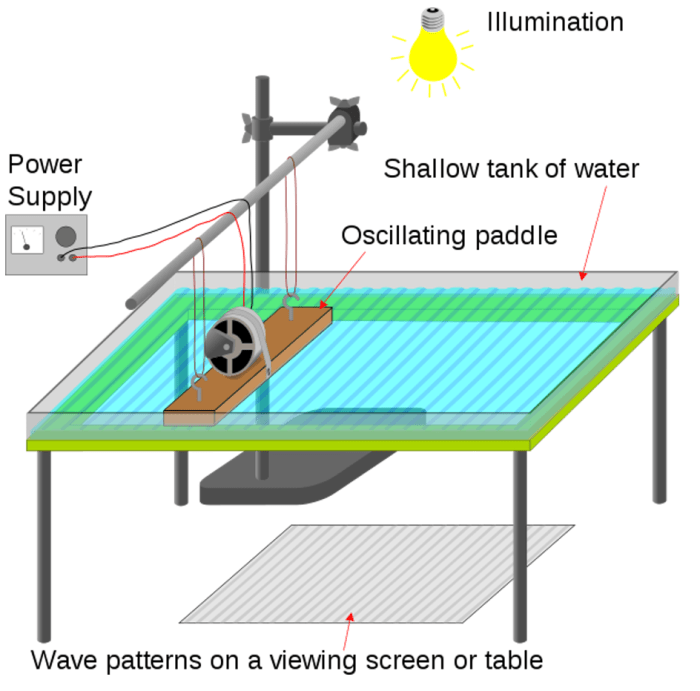
This answer key provides explanations and answers to the questions in the Gizmo ripple tank simulation.
Questions and Answers
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the wavelength of a ripple? | The distance between two adjacent crests or troughs. |
| What is the frequency of a ripple? | The number of crests that pass a fixed point in one second. |
| What is the speed of a ripple? | The distance traveled by a ripple in one second. |
| What is the relationship between wavelength, frequency, and speed? | Speed = Wavelength
|
| How does the wavelength of a ripple change as it travels through a narrower opening? | The wavelength decreases. |
| How does the frequency of a ripple change as it travels through a narrower opening? | The frequency remains the same. |
| How does the speed of a ripple change as it travels through a narrower opening? | The speed decreases. |
Ripple Tank Applications: Gizmo Ripple Tank Answer Key
Ripple tanks have various applications in different fields, including physics, engineering, and acoustics. They are used to demonstrate and study wave phenomena, including wave propagation, interference, diffraction, and reflection.
Education and Research
- In physics education, ripple tanks are used to demonstrate wave properties and principles. Students can observe and analyze wave patterns, measure wavelengths, and determine wave speeds.
- In research, ripple tanks are employed to study wave behavior in complex environments, such as the effects of obstacles or boundaries on wave propagation.
Engineering
- In civil engineering, ripple tanks are used to simulate and study wave forces on structures, such as dams, bridges, and coastal defenses.
- In mechanical engineering, ripple tanks are employed to investigate fluid flow patterns and acoustics.
Acoustics
- In architectural acoustics, ripple tanks are used to design and optimize sound propagation in concert halls, theaters, and other performance spaces.
- In underwater acoustics, ripple tanks are used to study sound wave propagation in the ocean and to locate underwater objects.
Ripple Tank Physics
Ripple tanks are a valuable tool for studying the physics of waves. They consist of a shallow tank filled with water, with a wave generator at one end. The waves generated by the wave generator travel across the water’s surface, creating ripples.
The physics of ripple tanks is based on the principles of wave propagation and interference. Wave propagation refers to the movement of waves through a medium. In the case of ripple tanks, the medium is water. Interference refers to the interaction of two or more waves, which can result in constructive or destructive interference.
Wave Propagation
Waves are disturbances that travel through a medium. They are characterized by their wavelength, frequency, and amplitude. The wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of the wave. The frequency is the number of waves that pass a given point in a given amount of time.
The amplitude is the height of the wave from the trough to the crest.
In ripple tanks, waves are generated by the wave generator. The wave generator creates a disturbance in the water, which causes the water molecules to move up and down. This movement creates a wave that travels across the water’s surface.
Interference
Interference is the interaction of two or more waves. When two waves interact, they can either reinforce each other or cancel each other out. Constructive interference occurs when the crests of two waves line up, resulting in a wave with a larger amplitude.
The Gizmo Ripple Tank Answer Key is a valuable resource for understanding the principles of wave interference and diffraction. The answer key provides step-by-step instructions for conducting experiments and analyzing results. Additionally, it offers insights into the gamma phi beta hand symbol , which represents the fraternity’s values of friendship, leadership, and service.
By utilizing the Gizmo Ripple Tank Answer Key, students can deepen their understanding of wave phenomena and gain a greater appreciation for the scientific method.
Destructive interference occurs when the crests of two waves line up with the troughs of two other waves, resulting in a wave with a smaller amplitude.
In ripple tanks, interference can be observed by placing two wave generators at different points in the tank. The waves generated by the two wave generators will interact, creating areas of constructive and destructive interference.
Ripple Tank Experiments
A ripple tank is a device that allows us to visualize and study the propagation of waves. It consists of a shallow water tank with a wave generator at one end. The waves are generated by a vibrating paddle or a speaker, and they travel across the water surface.
The waves can be reflected, refracted, or diffracted by obstacles placed in the tank. Ripple tanks are used to demonstrate wave phenomena such as interference, diffraction, and refraction.
Design a series of experiments that can be conducted using a ripple tank
Here are a few experiments that can be conducted using a ripple tank:
- Reflection of waves:In this experiment, a wave is generated and allowed to reflect off a barrier placed in the tank. The angle of incidence is measured, and the angle of reflection is observed. The law of reflection can be verified by comparing the two angles.
- Refraction of waves:In this experiment, a wave is generated and allowed to pass through a barrier with a different refractive index. The change in the direction of the wave is observed, and the law of refraction can be verified.
- Diffraction of waves:In this experiment, a wave is generated and allowed to pass through a narrow slit or around an obstacle. The spreading out of the wave is observed, and the diffraction pattern can be analyzed.
- Interference of waves:In this experiment, two waves are generated and allowed to interact with each other. The interference pattern is observed, and the principle of superposition can be verified.
- Standing waves:In this experiment, a wave is generated and allowed to reflect off a barrier at the other end of the tank. The standing wave pattern is observed, and the nodes and antinodes can be identified.
Provide step-by-step instructions for each experiment
The step-by-step instructions for each experiment will vary depending on the specific experiment being conducted. However, the general steps are as follows:
- Set up the ripple tank and fill it with water.
- Generate a wave using the wave generator.
- Place the obstacle or barrier in the tank.
- Observe the behavior of the wave as it interacts with the obstacle or barrier.
- Record your observations and analyze the data.
Include a table summarizing the experiments and their objectives
| Experiment | Objective |
|---|---|
| Reflection of waves | To verify the law of reflection |
| Refraction of waves | To verify the law of refraction |
| Diffraction of waves | To observe the diffraction pattern of waves |
| Interference of waves | To verify the principle of superposition |
| Standing waves | To observe the standing wave pattern |
Ripple Tank Data Analysis
Data analysis in ripple tank experiments involves organizing and interpreting the observed wave patterns to determine wave properties. The data can be recorded in a table and analyzed using various techniques to extract information about wavelength, frequency, and wave velocity.
Data Recording and Organization
To record data from ripple tank experiments, a table can be organized with the following columns:
- Experiment number
- Frequency of the wave source (Hz)
- Distance between wave crests (wavelength, m)
- Time taken for a certain number of waves to pass a fixed point (period, s)
- Number of waves passing a fixed point in a given time interval
Data Analysis Techniques, Gizmo ripple tank answer key
Once the data is recorded, it can be analyzed using various techniques to determine wave properties:
- Wavelength (λ):Measured directly from the ripple tank as the distance between two consecutive wave crests.
- Frequency (f):Calculated as the inverse of the period (f = 1/T), where T is the time taken for a certain number of waves to pass a fixed point.
- Wave Velocity (v):Calculated as the product of wavelength and frequency (v = λf).
- Wave Amplitude:Measured as the vertical displacement of the water surface from its equilibrium position.
Example Data Analysis
Consider the following data from a ripple tank experiment:
| Experiment | Frequency (Hz) | Wavelength (m) | Period (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 15 | 0.067 | 0.067 |
Using the data analysis techniques described above:
- Wavelength (λ) for Experiment 1: 0.1 m
- Frequency (f) for Experiment 1: 1/0.1 = 10 Hz
- Wave Velocity (v) for Experiment 1: λf = 0.1 m x 10 Hz = 1 m/s
Similar calculations can be performed for Experiment 2.
Ripple Tank Visualizations
Ripple tanks are used to visualize wave propagation and interference. By dropping a stone into a ripple tank, a series of waves is created that spread out in all directions. The waves can be reflected, refracted, and diffracted by obstacles in the tank, and they can also interfere with each other.
These effects can be used to demonstrate a variety of wave phenomena, including:
- Wave propagation:The waves in a ripple tank travel at a constant speed, and they can be reflected, refracted, and diffracted by obstacles in the tank.
- Wave interference:When two or more waves overlap, they can interfere with each other. This can result in constructive interference, which produces a larger wave, or destructive interference, which produces a smaller wave.
Visualizations of Wave Propagation and Interference
The following illustrations demonstrate the concepts of wave propagation and interference in ripple tanks. The illustrations use different colors and patterns to highlight different aspects of the waves.
- Wave propagation:The following illustration shows a series of waves propagating from a point source. The waves are shown as concentric circles, and the color of the waves indicates their amplitude.
- Wave reflection:The following illustration shows a wave reflecting off of a barrier. The reflected wave is shown as a new series of waves propagating away from the barrier.
- Wave refraction:The following illustration shows a wave refracting as it passes from one medium to another. The refracted wave is shown as a new series of waves propagating at a different angle.
- Wave diffraction:The following illustration shows a wave diffracting as it passes through a narrow opening. The diffracted wave is shown as a new series of waves propagating in all directions.
- Wave interference:The following illustration shows two waves interfering with each other. The resulting wave is shown as a new series of waves with a larger amplitude in some regions and a smaller amplitude in other regions.
FAQs
What is the purpose of a ripple tank?
A ripple tank is a device used to visualize and study wave phenomena, such as wave propagation, reflection, refraction, and interference.
How does a ripple tank work?
A ripple tank consists of a shallow water-filled tank with a wave generator at one end. The wave generator creates ripples that propagate across the water’s surface, allowing for the observation and analysis of wave behavior.
What are the applications of ripple tanks?
Ripple tanks are used in various fields, including physics education, acoustics, and oceanography. They help demonstrate wave properties, study wave interactions, and analyze wave behavior in different media.